- MTTReport
- Posts
- Building AI's central nervous system
Building AI's central nervous system
PLUS: Amazon's thinking storage, controlling AI agents, and the verdict on 'vibe hacking'

Good morning, Security enthusiast!
A company building the 'central nervous system' for AI data centers just secured a major funding round. NetBox Labs' platform aims to automate and manage the vast, complex networks that power the current AI boom.
The funding highlights a critical, often-overlooked aspect of AI development: the foundational plumbing. As companies race to deploy AI, will the winners be those with the best models, or those who master the underlying network infrastructure first?
In today’s Cyber Security recap:
Building AI's foundational 'nervous system'
Amazon’s S3 evolves into 'thinking storage'
A new protocol for controlling AI agents
The current state of AI 'vibe hacking'
AI's Nervous System

The Recap: NetBox Labs, the company behind the popular open-source network management tool, secured $35 million to scale its platform. The company provides a “central nervous system” for automating and managing the massive data center networks required for AI workloads.
Unpacked:
The platform offers a single source of truth, replacing the messy spreadsheets many organizations still use for critical tasks like device provisioning and IP address management.
AI infrastructure provider CoreWeave uses NetBox to accelerate its deployment timelines, noting that efficiency gains from faster builds directly impacts our revenue.
Recent updates show the platform's forward momentum, adding features for automated network discovery and even an agentic AI operations tool to accelerate automation for networking teams.
Bottom line: This funding highlights the critical importance of building robust foundational infrastructure to support the AI boom. Tools that automate network management are becoming indispensable for companies racing to scale their AI operations securely and efficiently.
Amazon's Thinking Storage

The Recap: Amazon Web Services is transforming its core S3 storage into an AI-native platform. The upgrade introduces S3 Tables and a queryable metadata lake, enabling AI agents to intelligently find and process data directly.
Unpacked:
The new S3 Tables feature, built on the open-source Apache Iceberg format, lets you run standard SQL queries directly on data files without needing to move them into a separate data warehouse.
AWS envisions a future driven by autonomous data-AI agents that can locate, transform, and act on information, with companies like StarHub already using them to process insurance workflows.
A new "metadata lake" stores descriptive tags and summaries about your files, allowing AI agents to quickly discover relevant data by querying the metadata first instead of the massive underlying files.
Bottom line: S3 is evolving from a passive data repository into an active, intelligent data platform. This shift allows businesses to build more powerful AI applications and automate complex data-driven tasks with greater speed and efficiency.
Leashing the AI Agents
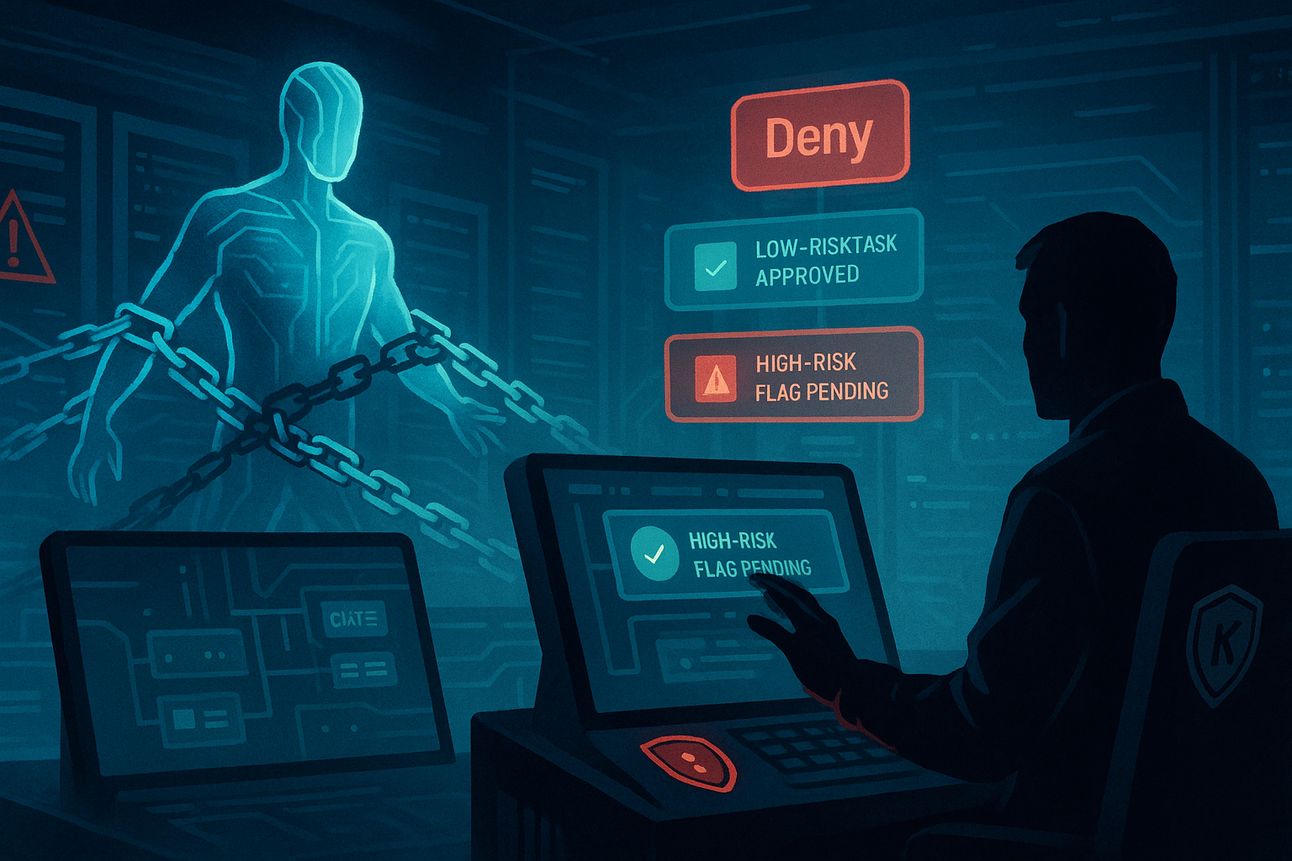
The Recap: Keeper Security is tackling the risk of autonomous AI agents by launching a new protocol for its Secrets Manager. The system enables policy-driven, auditable control over how AI tools access sensitive credentials.
Unpacked:
The protocol enforces a human-in-the-loop model, ensuring sensitive actions like creating or deleting secrets always require human confirmation.
It supports a graduated autonomy model, allowing agents to handle low-risk tasks independently while flagging high-risk actions for approval.
The system is built for multi-tenant environments, allowing MSSPs and IT teams to enforce isolated, client-specific security policies.
Bottom line: This provides a practical solution to one of the biggest security hurdles in deploying AI agents for real work. It offers a clear blueprint for companies to embrace automation without handing over the keys to the kingdom.
The 'Vibe Hacking' Verdict
The Recap: A new study finds that while AI can't yet autonomously "vibe hack"—find vulnerabilities and write exploits—the technology is improving so quickly that this could soon change. Forescout's extensive testing shows current models still need significant human guidance for complex security tasks.
Unpacked:
Researchers tested over 50 different LLMs, including commercial models, open-source versions, and underground models like WormGPT advertised to cybercriminals.
Commercial models performed the best, with newer reasoning models like DeepSeek V3 successfully creating functional exploits, while most other models struggled or failed.
The next big leap may come from agentic AI, which lets models chain together multiple tools and actions, overcoming current roadblocks in complex tasks like exploit development.
Bottom line: The barrier for creating exploits hasn't been lowered for most attackers—for now. This research serves as a clear signal for defenders to double down on fundamentals before AI makes launching advanced attacks much easier.
The Shortlist |
|---|
Researchers breached xAI's new Grok-4 model within 48 hours of its launch, using a combination of "Echo Chamber" and "Crescendo" jailbreak techniques to bypass its safety filters.
Gigabyte faces newly disclosed UEFI firmware vulnerabilities that allow attackers to execute arbitrary code in the highly privileged System Management Mode (SMM), creating a risk of undetectable, persistent bootkits.
Accenture expanded its partnership with Microsoft to embed generative AI directly into security operations, aiming to modernize SOCs with tools built on Microsoft Sentinel, Defender, and Entra.
Researchers unveiled a new forensic method to track attackers' lateral movements by analyzing RDP bitmap cache files, allowing investigators to reconstruct the exact screen images viewed during a session.